Analog computers having many advantages in signal processing, such as real-time processing, continuous data representation, high-speed operations, accuracy, nonlinear signal manipulation, high-fidelity signal synthesis, and hardware-level interactions. These advantages make analog computers highly relevant in signal processing tasks that require real-time processing, high fidelity, and interactions with physical systems. In this article, we will explore the advantages of analog computers in signal processing and understand their relevance in this domain.
Signal processing plays a vital role in various applications, including telecommunications, audio analysis, image processing, and control systems. Analog computers offer specific advantages in signal processing tasks, providing real-time processing, continuous data representation, high-speed operations, accuracy, and compatibility with physical systems. While digital signal processing dominates the field, analog computers continue to excel in certain signal processing applications where their unique benefits are highly valued.
what is Analog Computers?
Analog computers utilize continuous physical quantities, such as voltages or currents, to represent and manipulate data. Unlike digital computers that operate on discrete values, analog computers can directly model and process signals in their continuous form. This inherent ability makes analog computers well-suited for signal processing tasks that involve the manipulation and analysis of continuous signals.
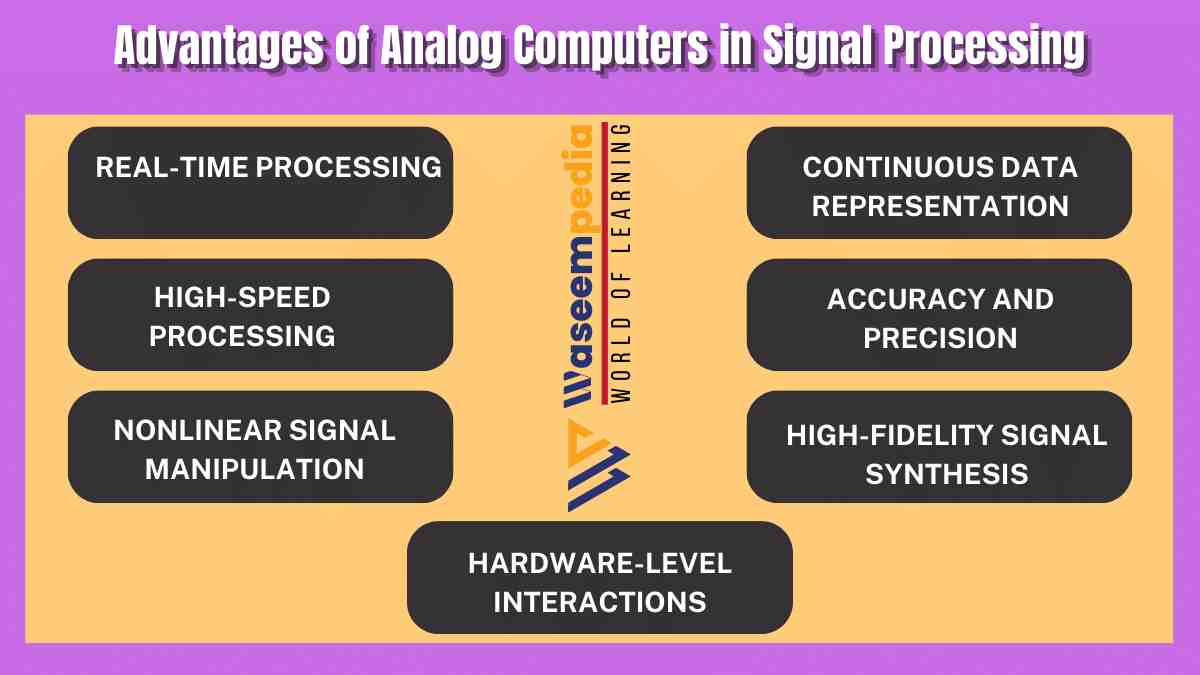
7 Advantages of Analog Computers in Signal Processing
7 Advantages of Analog Computers in Signal Processing are as follows.
1. Real-Time Processing
Real-time processing is a one of the most important Advantages of Analog Computers in Signal Processing. It is a critical requirement in signal processing applications, particularly those involving live or time-dependent signals. Analog computers excel in real-time processing due to their ability to work with continuous data streams without the need for digitization or discretization.
This real-time capability allows analog computers to provide immediate responses and feedback, making them ideal for tasks such as real-time filtering, modulation, and control in signal processing applications.
2. Continuous Data Representation
Analog computers utilize continuous data representation, allowing them to preserve the fidelity of signals without the need for quantization or sampling. In signal processing, where accurate representation and analysis of signals are crucial, analog computers shine.
By working with continuous signals, analog computers can capture and manipulate the fine-grained details of signals, enabling high-fidelity processing and analysis. This continuous data representation contributes to more accurate and realistic signal processing outcomes.
3. High-Speed Processing
Analog computers are known for their high-speed processing capabilities. The analog nature of computation allows for rapid signal manipulation without the overhead of converting between analog and digital representations.
Analog computers can perform signal processing operations at high speeds, making them well-suited for tasks that require real-time processing or dealing with high-frequency signals. This advantage enables efficient and effective signal processing in time-critical applications.
4. Accuracy and Precision
Analog computers offer high levels of accuracy and precision in signal processing. By working with continuous signals, analog computers can accurately represent and manipulate signals without the quantization errors associated with digital systems.
This accuracy and precision are particularly valuable in signal processing tasks that require faithful reproduction of signal characteristics, such as filtering, amplification, and modulation. Analog computers enable fine-grained control and enhance the accuracy of signal processing operations.
5. Nonlinear Signal Manipulation
Nonlinear signal processing is essential in various applications, including audio effects, image enhancement, and nonlinear control systems. Analog computers are well-suited for nonlinear signal manipulation due to their ability to directly model and process nonlinear relationships between signal variables.
By leveraging the analog nature of computation, analog computers enable researchers and engineers to explore complex nonlinear signal transformations and achieve unique signal processing effects that may be challenging to achieve with digital systems.
6. High-Fidelity Signal Synthesis
Analog computers excel in high-fidelity signal synthesis, allowing for accurate generation of complex waveforms and signals. By combining various analog components and circuitry, researchers can design analog computers that generate signals with high precision and fidelity.
This capability is particularly valuable in applications such as audio synthesis, where analog computers can produce rich and nuanced sound waves that closely resemble real-world audio signals. Analog computers enable researchers to create signals with high-quality reproduction and fine control. So, High-Fidelity Signal Synthesis is also a very important Advantages of Analog Computers in Signal Processing.
7. Hardware-Level Interactions
Analog computers enable hardware-level interactions in signal processing tasks, providing direct connections to physical components and systems. Researchers and engineers can integrate analog computers with sensors, actuators, and other physical devices to perform real-time signal processing and control.
This hardware-level interaction allows for seamless integration with physical systems, facilitating accurate measurement, signal conditioning, and control operations. Analog computers provide a closer coupling between signal processing algorithms and the physical world, enhancing the effectiveness of signal processing tasks.
Related FAQ’s
How do analog computers differ from digital computers in signal processing?
Analog computers process continuous signals directly, while digital computers operate on discrete values and require quantization or sampling for signal processing.
What advantages do analog computers offer in signal processing?
Analog computers excel in real-time processing, continuous data representation, high-speed operations, accuracy, nonlinear signal manipulation, high-fidelity signal synthesis, and hardware-level interactions.
Why is real-time processing important in signal processing?
Real-time processing enables immediate responses and feedback, making it crucial for tasks such as real-time filtering, modulation, and control in signal processing applications.
How do analog computers ensure accuracy and precision in signal processing?
Analog computers work with continuous signals, allowing for accurate representation and manipulation without the quantization errors associated with digital systems.
Why are hardware-level interactions valuable in signal processing?
Hardware-level interactions enable direct connections to physical components and systems, facilitating accurate measurement, signal conditioning, and control operations in signal processing tasks.