Plant growth promotion is essential for maximizing crop yields, enhancing plant health, and ensuring sustainable agriculture. While various factors influence plant growth, bacteria play a vital role in promoting plant growth through their interactions with plants.
Beneficial bacteria can enhance nutrient availability, stimulate hormone production, improve stress tolerance, and protect plants from pathogens.
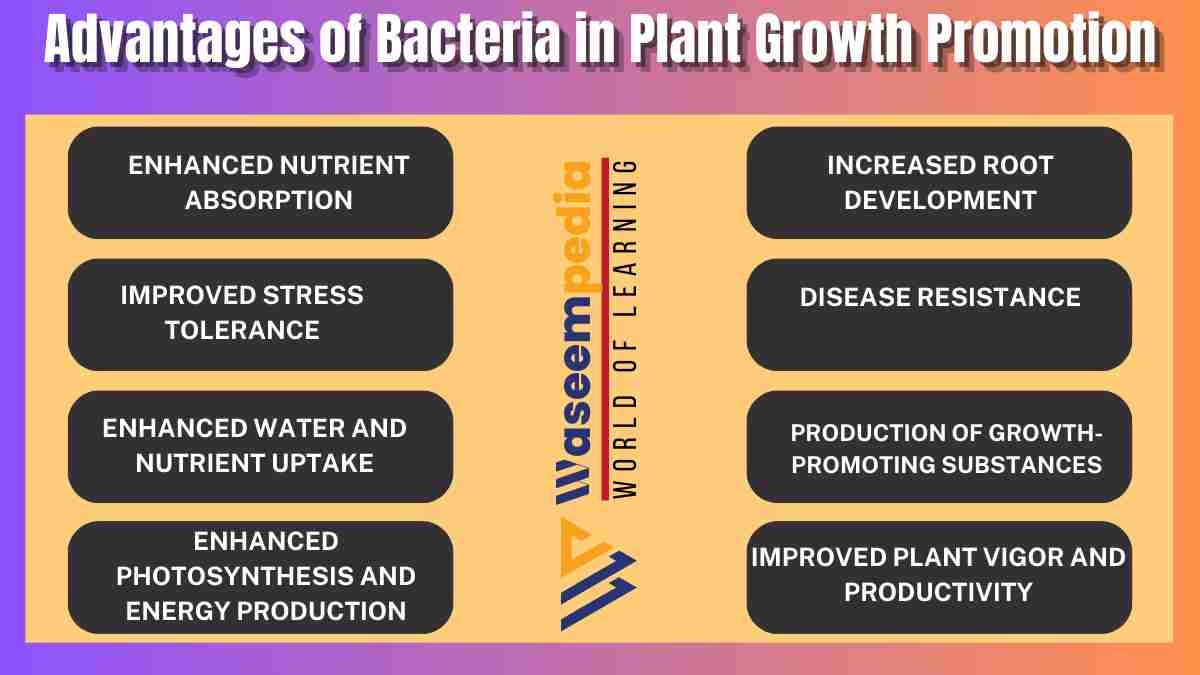
Bacteria offer significant advantages in promoting plant growth and optimizing crop production. Through their contributions to nutrient availability, hormone production, stress tolerance enhancement, biological control of pathogens, improved root development, and environmental adaptation, bacteria play a crucial role in supporting healthy plant growth and ensuring sustainable agriculture.
Harnessing the potential of bacteria in plant growth promotion is key to maximizing yields, minimizing chemical inputs, and fostering environmentally friendly farming practices.
In this article, we will read the advantages of bacteria in plant growth promotion and highlight their significant contributions.
Introduction of Bacteria in Plant Growth Promotion
Plant growth promotion involves the enhancement of plant development and productivity. Bacteria, as beneficial members of the plant microbiome, can positively influence plant growth through various mechanisms. Understanding the advantages of bacteria in plant growth promotion is crucial for sustainable agriculture and optimizing crop production.
Understanding Plant Growth Promotion
Plant growth promotion encompasses a range of processes that facilitate healthy plant development. It involves the stimulation of root growth, nutrient uptake, hormone production, stress tolerance, and protection against pathogens. Bacteria contribute significantly to plant growth promotion through their interactions with plants and the surrounding soil environment.
1. Bacteria’s Role in Nutrient Availability
One of the primary advantages of bacteria in plant growth promotion is their ability to enhance nutrient availability in the soil. Bacteria contribute to nutrient cycling by decomposing organic matter and releasing essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, into forms that are easily accessible to plants.
Through their enzymatic activities, bacteria break down complex compounds and convert them into simpler forms that can be readily absorbed by plant roots.
2. Hormone Production and Regulation
Bacteria can produce and regulate plant growth hormones, including auxins, cytokinins, and gibberellins. These hormones influence various aspects of plant growth, such as cell division, root development, flowering, and fruiting. Beneficial bacteria can stimulate hormone production or alter the plant’s hormone balance, promoting optimal growth and development.
3. Enhanced Stress Tolerance
Bacteria play a crucial role in enhancing plants’ tolerance to various environmental stresses. Beneficial bacteria can produce compounds that protect plants against stressors such as drought, salinity, extreme temperatures, and pathogen attacks. These bacteria also induce the plant’s natural defense mechanisms, enabling it to withstand and recover from stressful conditions more effectively.
4. Biological Control of Pathogens
Certain bacteria possess the ability to suppress plant diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms. They can compete with harmful pathogens for resources, produce antimicrobial compounds, and induce systemic resistance in plants. By colonizing the plant’s roots and surrounding soil, beneficial bacteria provide a protective barrier, reducing the risk of pathogen establishment and promoting healthier plant growth.
5. Improved Root Development
Bacteria contribute to improved root development, which is crucial for nutrient and water uptake. Beneficial bacteria can stimulate root growth, increase root surface area, and facilitate the formation of root hairs. These changes enhance the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients and water from the soil, promoting robust plant growth and productivity.
6. Environmental Adaptation
Bacteria possess remarkable adaptability to diverse environmental conditions. Beneficial bacteria can thrive in different soil types, pH levels, temperature ranges, and nutrient availability. This adaptability allows bacteria to provide consistent plant growth promotion benefits across varying agricultural environments, making them valuable allies in sustainable farming practices.